Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid, or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solvent to form a homogeneous solution of the solute in the solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the used solvent as well as on temperature and pressure. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is measured as the saturation concentration where adding more solute does not increase the concentration of the solution.
Process of solubilisation:
The
process of solubilisation involves the breaking of inter-ionic or
intermolecular bonds in the solute, the separation of the molecules of the
solvent to provide space in the solvent for the solute, interaction between the
solvent and the solute molecule or ion.
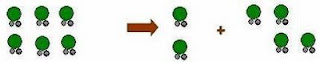
Step 1:
Holes opens in the solvent
Step2:
Molecules of the solid breaks away from the bulk
Step 3:The
freed solid molecule is intergrated into the hole in the solvent